Gallstones: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
What Are Gallstones?
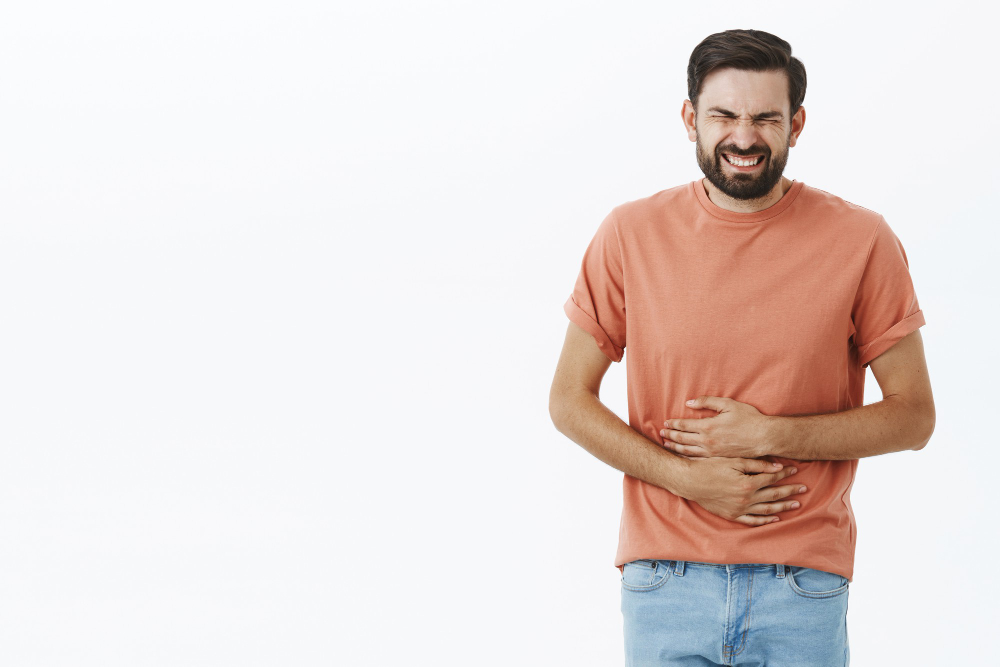
Gallstones are small, hard pieces that form in the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ under your liver. It stores bile, which helps digest fat. Sometimes, bile can harden and turn into stones. These stones can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. Gallstones are common, and many people do not know they have them. However, some people may develop symptoms that need medical care.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Many people with gallstones have no symptoms. But, when a stone blocks a bile duct, symptoms can appear. Early treatment can help prevent problems. Common gallstones symptoms include:Pain in the upper right side of the bellyPain that spreads to the back or right shoulderNausea or vomitingSudden, sharp pain after eating fatty foodsYellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)Fever or chills
Sometimes, symptoms come and go. If pain lasts more than a few hours, you should seek medical help.
Causes and Risk Factors
Gallstones form when the balance of substances in bile changes. For example, too much cholesterol or bilirubin can cause stones. Several risk factors increase your chance of getting gallstones. These include:Being overweight or obeseEating a high-fat or high-cholesterol dietLosing weight very quicklyBeing female, especially during pregnancyBeing over age 40Having a family history of gallstonesHaving diabetes
Even so, some people get gallstones without any risk factors. Knowing your risks can help you make healthy choices.
How Gallstones Are Diagnosed
If you have symptoms, your doctor may suggest tests for gallstones diagnosis. Early diagnosis can prevent complications. Common tests include:Ultrasound: This safe test uses sound waves to look for stones in the gallbladder.Blood tests: These can show signs of infection or blocked bile ducts.CT scan or MRI: These images help find stones or other problems.
Sometimes, doctors use other tests to check the bile ducts. Your doctor will choose the best test for you.
Treatment Options for Gallstones
Treatment depends on your symptoms and health. If you have no symptoms, you may not need treatment. However, if you have pain or other problems, treatment is needed. Gallstone treatment options include:Medications: Some medicines can dissolve small stones, but this takes time.Surgery: Removing the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is the most common treatment. It is safe and effective.Non-surgical procedures: In rare cases, doctors use special tools to remove stones without surgery.
Most people recover well after treatment. Your doctor will explain the best option for you.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
While you cannot prevent all gallstones, healthy habits can lower your risk. For example, you can:Eat a balanced diet with plenty of fiberLimit fatty and fried foodsMaintain a healthy weightLose weight slowly, if neededStay active with regular exercise
Making small changes can help keep your gallbladder healthy. If you have questions, ask your doctor for advice on how to prevent gallstones.
When to See a Doctor
Sometimes, gallstones can cause serious problems. You should see a doctor if you have:Severe or lasting belly painYellowing of the skin or eyesFever with chillsVomiting that does not stop
Early care can prevent complications. If you live in a city with gallstones treatment options, seeking timely medical attention is important.
If you suspect you have gallstones, consult a specialist at SIDS Hospital for personalized guidance and proper care.


 Book Appointment
Book Appointment.png) Video Consultation
Video Consultation
