Understanding Urinary Bladder Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
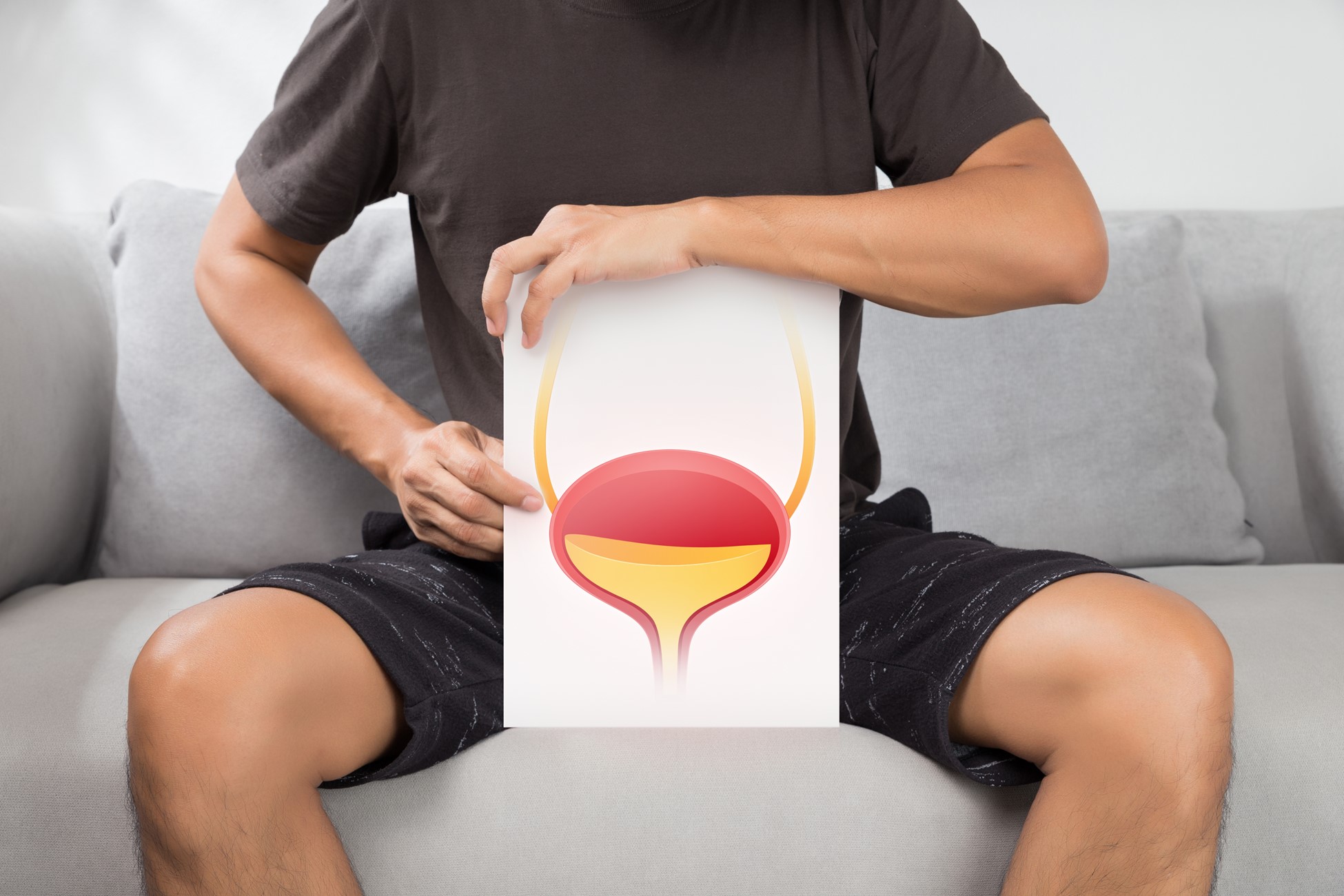
Urinary bladder cancer is a disease that involves the uncontrolled growth of cells in the bladder, a small organ in the lower abdomen that collects urine from the kidneys before it is excreted from the body. It’s vital for the public to be aware of this type of cancer due to its potential impact on health. Detecting and treating urinary bladder cancer early can significantly enhance outcomes and survival rates for patients. Awareness can lead to timely medical consultation, which is paramount in preventing severe complications.
Introduction to Urinary Bladder Cancer
Urinary bladder cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow in this organ’s inner lining. This cancer type is important to understand because it can progress and spread if not detected early. Certain individuals are more at risk than others.
Men are more often diagnosed with urinary bladder cancer than women, and the risk increases with age, typically affecting those over 55. Additionally, people who smoke and those with a history of chemical exposure are more susceptible. Learning about cancer can help reduce risk through informed lifestyle choices and timely checkups.
Prevalence and Statistics
Urinary bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men in the United States. Estimates show tens of thousands of new cases annually. The disease also claims many lives, making it a critical health concern.
Globally, rates are also significant, though they vary by region. Gender differences exist, as men are more likely to develop urinary bladder cancer than women. The elderly are also at a higher risk, underlining the importance of regular medical examinations and awareness for those demographics.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors could lead to urinary bladder cancer. Smoking is a significant cause, as it exposes the body to harmful chemicals that affect the bladder lining. Workplace chemical exposure also poses risks, especially in industries like paint, rubber, and textiles.
Beyond lifestyle or work-related exposures, some infections can contribute to the risk. Urinary bladder cancer may also occur due to genetic predispositions. People with close relatives who have had cancer may have higher chances of developing it themselves.
These risks can vary by location. Cultural habits, diets, and even pollution levels in different regions contribute to the likelihood of exposure. Understanding and minimizing these risks can be crucial for prevention.
Identifying Symptoms Early
Recognizing symptoms early in urinary bladder cancer can save lives. The most common symptom is blood in the urine, a condition known as hematuria. Other signs include frequent urination, pain during urination, and back pain.
Unfortunately, these symptoms are sometimes confused with other less severe conditions. This confusion can delay seeking medical help. Consulting a doctor when symptoms appear is crucial for correct diagnosis and timely treatment. Early intervention can result in better management and outcome.
Diagnosis and Staging
Diagnosing urinary bladder cancer involves several procedures and tests. Doctors often use urine tests, imaging scans, and biopsies to confirm cancer. Medical professionals also perform cystoscopies, which involve using a small camera to look inside the bladder.
Once diagnosed, urinary bladder cancer is categorized into different stages. Staging assesses how much the cancer has spread. This information is essential as it guides the treatment plan, helping determine whether a patient requires surgery, chemotherapy, or other interventions.
Treatment Modalities
Treatment for urinary bladder cancer varies depending on the stage. Early stages may only require surgery to remove the cancerous parts of the bladder. Chemotherapy or immunotherapy might follow to ensure the disease doesn’t return.
As cancer progresses, more extensive surgeries or complete bladder removal might be necessary. Chemotherapy or radiation is often used to kill leftover cancer cells. Emerging treatments, like targeted therapies, show promise.
These innovative treatments zero in on specific cancer traits, potentially reducing side effects and improving efficacy. Staying informed about these options can empower patients to make knowledgeable treatment decisions.
Living With Bladder Cancer: Management and Support
Living with urinary bladder cancer involves understanding the prognosis and survival rates, which vary based on several factors, including stage and early detection. It is vital for patients to engage in regular follow-up care. Continuous monitoring helps spot any recurrence promptly.
Patients are encouraged to adopt a healthy lifestyle, which involves proper dieting and quitting smoking to aid recovery. Support groups and counseling can provide emotional assistance and aid in managing stress during this challenging journey.
Prevention: Reducing Risk and Promoting Awareness
Preventive measures can make a notable difference in reducing the risk of urinary bladder cancer. Quitting smoking tops the list as a significant preventive strategy. Awareness about occupational hazards and ensuring workplace safety is equally essential.
Regular medical checkups, especially for those with higher risk profiles, enhance early detection chances. Educating oneself about the disease and its symptoms increases the likelihood of earlier interventions.
✅ Take charge of your urological health today –
📍 Visit SIDS Hospital for expert consultation and preventive care!
Conclusion
Urinary bladder cancer requires attention due to its severe health implications. Early detection and understanding cancer can lead to proactive steps, reducing risk and improving survival rates. Lifestyle adjustments, regular checkups, and seeking early medical advice are crucial. For further information, explore various support groups and health organizations to find reliable resources and connect with those who can help.


 Book Appointment
Book Appointment.png) Video Consultation
Video Consultation
